Why do some people stay married for decades while others jump from one relationship to the next? If humans are like rodents, recent research suggests that neuropeptides may help forge the ties that bind.
FOLLOWING VOLE BEHAVIOR
The vole, which inhabits many grasslands in the United States, is a rodent resembling a mouse but related to the lemming. Males in some vole species (such as meadow voles) show no partner preference whereas males in other species prefer one partner, share the same nest with her, and help care for their offspring.1
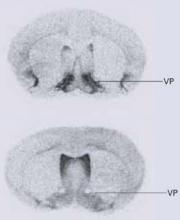
The neuropeptides oxytocin and arginine vasopressin are mediators of pair bonding. The brain of a prairie vole—a species in which males tend to bond with female partners—has more vasopressin receptors than that of the solitary meadow vole (Figure 1).
Figure 1 More vasopressin in bonding voles
Ventral forebrain autoradiograms show greater vasopressin (VP) expression in prairie voles (top) than meadow voles.
Reprinted with permission. © 2004, Nature Publishing Group.Lim et al, however, found that meadow voles were more likely to bond with a single female after the males’ vasopressin receptors were increased.2 The researchers isolated and replicated the gene sequence responsible for the vasopressin receptor in the prairie vole. Then, using a viral vector, they injected the gene into the ventral pallidum of 11 male meadow voles. Eleven other voles received placebo.
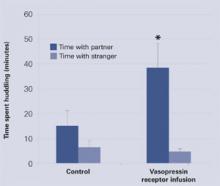
Two weeks later, each sexually naïve male vole was housed for 24 hours with a sexually receptive female vole. Then, each male was placed for 3 hours in a three-chamber apparatus with the partner female in one chamber and a novel female in another. The time spent huddling with each female was recorded.
Across 3 hours, the placebo group voles spent 10 to 15 minutes with either female—normal behavior for this species. By contrast, the voles that received the vasopressin receptors spent approximately 40 minutes with their partners but only about 5 minutes with the novel voles, thus showing more affiliative behavior and a clear preference for their mates (Figure 2). The findings suggest that the researchers may have produced a profound change in social behavior by altering one gene.
IMPLICATIONS FOR HUMANS
How this research relates to humans is unknown, as there is no sound evidence of a link between vole and human pair bonding. Likewise, the influence of the higher cortical areas in orchestrating human behaviors cannot be underestimated.
Neuroimaging, however, has shown that brain regions rich with oxytocin and vasopressin receptors are activated while a person views pictures of loved ones.3 Additionally, mens’ vasopressin levels have been shown to increase when they are sexually aroused.4 Whether these findings one day lead to a medicine that promotes monogamous behavior in men remains to be seen.5
Figure 2 Male meadow voles’ interactions with females after vasopressin or placebo treatment
Source: Adapted from reference 2